Menopause and HRT
What are the symptoms of the menopause❓
 Hot flushes 😰
Hot flushes 😰
 Night sweats 💤
Night sweats 💤
 Mood changes (low mood/anxiety)
Mood changes (low mood/anxiety)
 Difficulty/disturbances sleeping 💤
Difficulty/disturbances sleeping 💤
 Cognitive disturbances (memory loss/difficulty concentrating)
Cognitive disturbances (memory loss/difficulty concentrating)
 Libido loss (sex drive)
Libido loss (sex drive)
 Irregular menstruation
Irregular menstruation
 Dry vagina
Dry vagina
 Urination problems 💧
Urination problems 💧
 Aches and pains of joints/muscles
Aches and pains of joints/muscles
How is the menopause diagnosed❓
- Usually based on the clinical symptoms & age; but beware the following;
- Abnormal bleeding needs investigating
- Consider differential diagnosis
- Arrange Follicle Stimulating Hormone for patients if:
- < 40: premature menopause (2 separate results, > 30 IU/L, between 4 and 8 weeks apart)
- < 45: early menopause (2 separate results, >30 IU/L, between 4 and 8 weeks apart)
- > 50: wants to stop taking hormonal contraception (1 > 30 IU/L result – patient can stop taking hormonal contraception in 12 months)
How is the menopause treated❓
Lifestyle changes:
 Regular exercise 🚴
Regular exercise 🚴
 Relaxation exercise
Relaxation exercise
 Stress reduction ⬇
Stress reduction ⬇
 Decrease alcohol intake
Decrease alcohol intake
 Smoking cessation 🚬
Smoking cessation 🚬
 Healthy BMI
Healthy BMI
 Improve sleep hygiene 💤
Improve sleep hygiene 💤
 Avoid vasomotor symptoms (e.g. spicy food)
Avoid vasomotor symptoms (e.g. spicy food)
HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy):
 Fist line therapy for low mood and vasomotor symptoms
Fist line therapy for low mood and vasomotor symptoms
 Also beneficial for musculoskeletal symptoms, low sex drive, bone mineral density and urogenital atrophy
Also beneficial for musculoskeletal symptoms, low sex drive, bone mineral density and urogenital atrophy
HRT alternative options:
 CBT – beneficial for low mood and anxiety symptoms 😢
CBT – beneficial for low mood and anxiety symptoms 😢
 Isoflavones – can be beneficial for hot flushes 😰
Isoflavones – can be beneficial for hot flushes 😰
 Avoid SSRIs, SNRIs and clonidine as first line therapy
Avoid SSRIs, SNRIs and clonidine as first line therapy
Are there any contraindications to HRT❓
 History of breast cancer or oestrogen-rich tumour
History of breast cancer or oestrogen-rich tumour
 Bleeding of vagina which is undiagnosed
Bleeding of vagina which is undiagnosed
 Arterial thromboembolic disease
Arterial thromboembolic disease
 Thrombophillia
Thrombophillia
 Endometrial hyperplasia which is untreated
Endometrial hyperplasia which is untreated
 Current/recurrent VTE
Current/recurrent VTE
 Liver disease
Liver disease
What are the risks of HRT❓
Breast cancer:
 Risk from lifestyle choices likely greater than from HRT 🚬
Risk from lifestyle choices likely greater than from HRT 🚬
 Greater risk with combined HRT than oestrogen only HRT
Greater risk with combined HRT than oestrogen only HRT
 Micronised progesterone likely safest progestogen
Micronised progesterone likely safest progestogen
VTE:
 Risk increased by HRT ⬆
Risk increased by HRT ⬆
 Oral HRT preparations increase risk ⬆
Oral HRT preparations increase risk ⬆
 Micronised progesterone likely safest progestogen
Micronised progesterone likely safest progestogen
CVD (Cardiovascular disease):
 Post-menopausal women most commonly die of CVD
Post-menopausal women most commonly die of CVD
 In women <65, HRT does NOT increase risk
In women <65, HRT does NOT increase risk
 HRT may be cardioprotective in younger women
HRT may be cardioprotective in younger women
Stroke (CVA):
 Oral HRT increases risk (transdermal HRT preparations are safest) ⬆
Oral HRT increases risk (transdermal HRT preparations are safest) ⬆
Ovarian Cancer:
 Risk slightly increased by HRT ⬆
Risk slightly increased by HRT ⬆
What are the different types of HRT❓
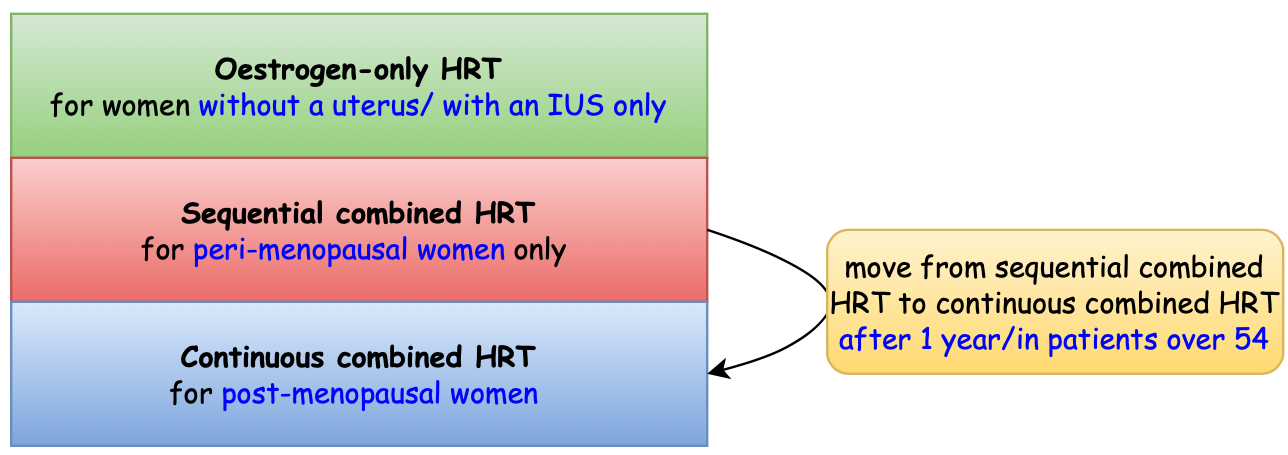
What type of HRT should I offer my patient❓
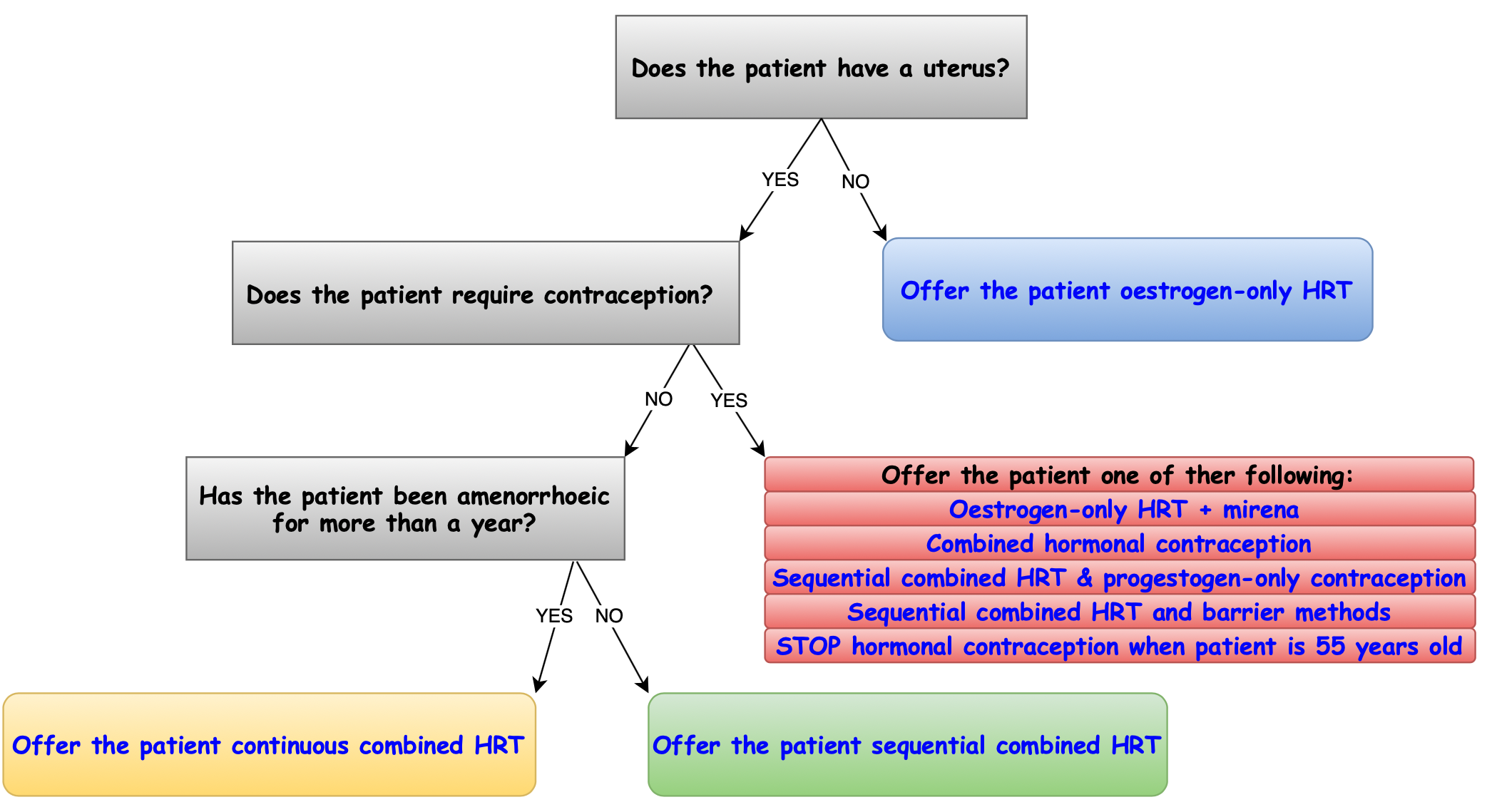
When should I review menopause treatment❓
 3 months after you start treatment 📅
3 months after you start treatment 📅
 Annually thereafter
Annually thereafter
What should I look for when reviewing a patient❓
- Ask the patient about any side effects, symptoms and indications
- Check patient’s blood pressure, BMI and screening
What if I identify problems when reviewing a patient❓
 Heavy bleeding on sequential HRT – increase progestogen dose/duration
Heavy bleeding on sequential HRT – increase progestogen dose/duration
 Bleeding on combined HRT – if remains after 3 to 6 months of it, try sequential HRT instead
Bleeding on combined HRT – if remains after 3 to 6 months of it, try sequential HRT instead
 Persistent bleeding more than 6 months after starting HRT – investigate the reason for this
Persistent bleeding more than 6 months after starting HRT – investigate the reason for this
 Side effects caused by progestogen – try alternative progestogen or IUS
Side effects caused by progestogen – try alternative progestogen or IUS
Summary:
- There are many symptoms of menopause which you should be aware of
- Menopause is usually diagnosed based on clinical symptoms and age
- Treatments: lifestyle changes, HRT or alternatives
- HRT risks: breast cancer, VTE, cardiovascular disease, stroke, ovarian cancer
- There are 3 types of HRT: oestrogen only, sequential combined and continuous combined
- You should review treatment 3 months after starting and annually thereafter