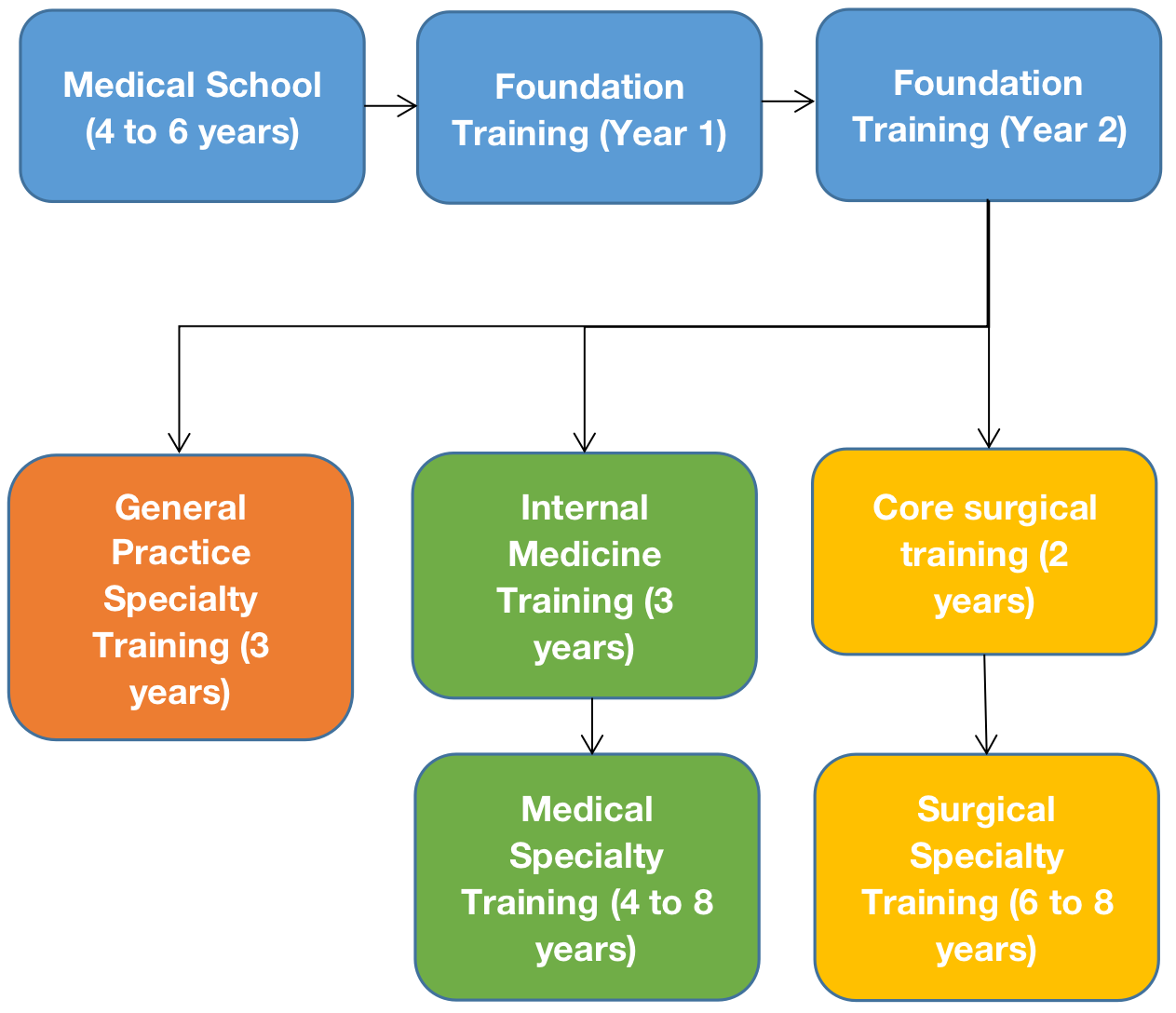
Stages of Medical Training
The Medical Training pathway varies depending on your chosen specialty, however, we have summarised a step by step guide to help you understand it.
Compulsory Training
Medical School:
Usually between 4 and 6 years depending on the stage of entry ⌛
4 years: graduate entry course 🎓
5 years: undergraduate course
6 years: undergraduate course with intercalated or foundation year
This is the first step which you must undertake in order to become a doctor in the UK
Foundation Training (FY1):
As a Medical School graduate, you will join the national foundation training programme in order to become a practicing doctor in the UK
You are a ‘junior doctor’
You receive provisional GMC registration and must complete a range of assessments and competencies to gain full GMC registration ✅
Focus in developing your skills and confidence managing patients 👍
Heavy supervision by senior doctors
Foundation Training (FY2):
By this stage, you will have full GMC registration ✅
You are a ‘junior doctor’
You will have greater independence and more responsibilities than in your first year
You can choose the specialties you wish to work
You are developing your skills for your future career

Further Training
When a doctor has successfully completed the foundation training programme, their training continues, either in general practice or a specialist area of medicine
General Practice Specialty Training:
3 years ⌛
You must apply to this at the end of your Foundation Training to become a UK GP 💻
You will have a range of jobs in hospitals and community GPs
The programme aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills to work as a GP 🧠
You must obtain a Certificate of completion of Training by passing the MRCGP examinations (Member of the Royal College of General Practitioners) 📃
As GP you must continually update your knowledge and keep up to date with new medical advancements and news 💻
If you have a specific interest, you may wish to undertake a diploma in this specialty
Internal Medical Training:
3 years ⌛
This programme is for doctors who wish to work as a specialist in a hospital 🏨
You will rotate between different medical specialties (of your choice) 🔄
You must pass the MRCGP examinations (Member of the Royal College of General Practitioners) by the end of the programme 📝
Medical Specialty Training:
6 to 8 years depending of specialty ⌛
You may apply for this when you have successfully completed IMT ✅
You will work within your chosen specialty for the entire programme
To become a consultant you must complete this training programme, passing all necessary competencied and complete the Fellow of the Royal College of physicians; you will then be awarded the CCT to apply for consultant posts ✅
Core Surgical Training:
2 years ⌛
This programme is for doctors who wish to become surgeons
You rotate among different specialties of your choice, most of which will be surgical 🔄
You must pass the MRCS examinations (Member of the Royal College of Surgeons) by the end of the programme ✅
Surgical Specialties Training:
6 to 8 years depending on specialty ⌛
You may apply for this when you have successfully completed CST ✅
Usually more competitive than GP and some medical specialties
You will continue to enhance your research and teaching skills, as well as attending conferences
You must complete the examinations for the FRCS (fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons); you will then be awarded the CCT to apply for consultant posts 📝
Summary
- An undergraduate or graduate entry medical degree followed by a 2 year foundation training programme is the beginning of any doctors career
- Following completion of the foundation training programme, a doctor can then choose to become a general practitioner, medical specialist or surgical specialist
- This is the normal medical training pathway for most doctors
- Flexible training or less than full time training is available
- There are also some training posts, which are not part of these training programmes but are educationally equivalent e.g. Locum Appointments for Training/Fixed Term Specialty Training Appointments