Measuring Vital Signs (OSCE)
Introduction
- Greet patient and introduce yourself
- Confirm patient details get patient consent ✍
- Wash hands ✋
- Check patient is not in any pain
Equipment
 Stopwatch ⏱
Stopwatch ⏱
 Thermometer 🌡
Thermometer 🌡
 NEWS2 chart
NEWS2 chart
 Pulse oximeter
Pulse oximeter
 Blood pressure monitor
Blood pressure monitor
What is NEWS2?
 Used to identify the risk of deterioration in adult patients ⬇
Used to identify the risk of deterioration in adult patients ⬇
Consists of 6 factors:
 Heart rate
Heart rate
 Respiration rate
Respiration rate
 Oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation
 Systolic blood pressure
Systolic blood pressure
 Consciousness
Consciousness
 Temperature 🌡
Temperature 🌡
Assess Heart Rate
- Palpate radial pulse 💓
- Assess rate and rhythm of radial pulse 💓
- Calculate heart rate from this:
- Measure radial pulse for 60 seconds (do this when rhythm is irregular) ⏱
- Measure radial pulse for 30 seconds and multiply by 2, or 15 multiplied by 4 ⏱
Normal vs abnormal heart rates:
 Normal: 60 to 100 bpm 💓
Normal: 60 to 100 bpm 💓
 Bradycardia: <60 bpm 💓
Bradycardia: <60 bpm 💓
 Tachycardia: >100 bpm 💓
Tachycardia: >100 bpm 💓
 Atrial fibrillation: irregular rhythm
Atrial fibrillation: irregular rhythm
Assess Respiratory rate
- Assess respiratory rate as you simultaneously palpate radial pulse 💓
- Identify differences between inspiration and expiration (e.g. prolonged expiration can indicate asthma or COPD)
- Assess for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 to measure the breaths per minute ⏱
Abnormal respiratory rate:
 Normal: 12-20 breaths per minute
Normal: 12-20 breaths per minute
 Bradypnoea: <12 breaths per minute
Bradypnoea: <12 breaths per minute
 Tachypnoea: >20 breaths per minute
Tachypnoea: >20 breaths per minute
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
- Switch on appropriately sized pulse oximeter/ remove nail varnish covering fingernail
- Put the pulse oximeter of the patient’s fingernail
- Record the oxygen saturation reading on the pulse spirometer
Target oxygen saturation:
 Scale 1: ≥96%
Scale 1: ≥96%
 Scale 2: 88 to 92% (used for patients at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure)
Scale 2: 88 to 92% (used for patients at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure)
Blood pressure
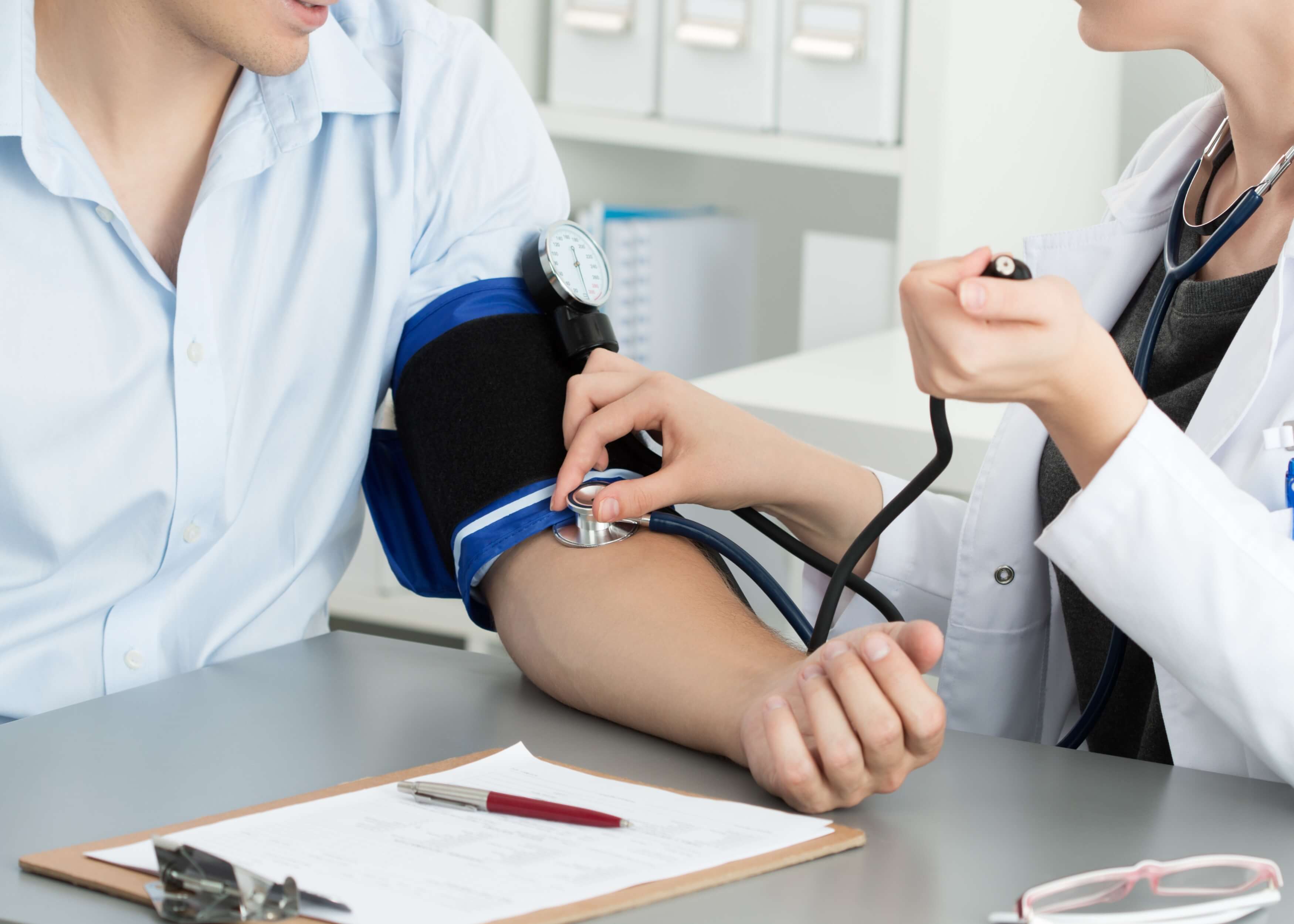
Blood pressure cuff:
- Select an appropriately sized blood pressure cuff
- Wrap the cuff around patient’s arm, with the marker in line with brachial artery
Manual measurement:
- Palpate radial pulse 💓
- Inflate cuff until you cannot feel the radial pulse 💓
- Record the estimate of systolic blood pressure on the sphygmomanometer
Accurate measurement:
- Position diaphragm of stethoscope over brachial artery
- Reinflate the cuff between 20 and 30 mmHg above the previously estimated systolic blood pressure ⬆
- Slowly deflate cuff (2 to 3 mmHg per second) ⬇
- Listen from the 1st Korotokoff sound, a thumping pulse 💓
- Record the pressure at this point, this gives you the systolic blood pressure
- Continue deflating the cuff until the sounds stop
- Record the pressure at the last sound, the 5th Korotokoff sound, this gives you the diastolic blood pressure
- Repeat on the opposite arm, after 2 minutes to confirm accuracy if the patient is hyper- or hypo-tensive
Consciousness
Use the ACVPU scale to establish the level of consciousness of the patient:
 Alert: fully alert patient, spontaneously opens eyes 👁
Alert: fully alert patient, spontaneously opens eyes 👁
 Confused: alert but confused patient ❓
Confused: alert but confused patient ❓
 Voices: patient responds to sound 👂
Voices: patient responds to sound 👂
 Pain: patient responds to pain
Pain: patient responds to pain
 Unresponsive: patient does not respond to sound or pain ❌
Unresponsive: patient does not respond to sound or pain ❌
Temperature
- Switch on a clean tympanic thermometer 🌡
- Apply a disposable cover to the probe end
- Place probe in ear canal 👂
- Insert the probe further inwards until it seals the ear canal 👂
- Make a note of the tympanic temperature 🌡
- Remove the probe and dispose of the cover
NEWS2
- Record the 6 measurements you have made on a NEWS2 chart ✍
- Calculate the NEWS2 score
Completion
- Tell the patient the examination is finished ✅
- Thank patient
- Wash hands ✋
- Summarise what the examination revealed ✍
Summary:
- Greet the patient and explain the procedure
- Assess Heart rate to identify tachycardia, bradycardia or atrial fibrillation
- Assess Respiration rate to identify bradypnoea or tachypnoea
- Assess Oxygen saturation to identify whether it is scale 1 or 2
- Assess Systolic blood pressure (manually or accurately)
- Assess Consciousness to identify whether the patient is: alert, confused, responds too sound/pain/neither
- Assess Temperature using a tympanic thermometer
Related Articles
This step by step guide is designed to take you through blood culture collection in OSCEs.
This step by step guide is designed to take you through how to take arterial bloods gas (ABG) in OSCEs.